ACNE STORY
Acne Vulgaris is …
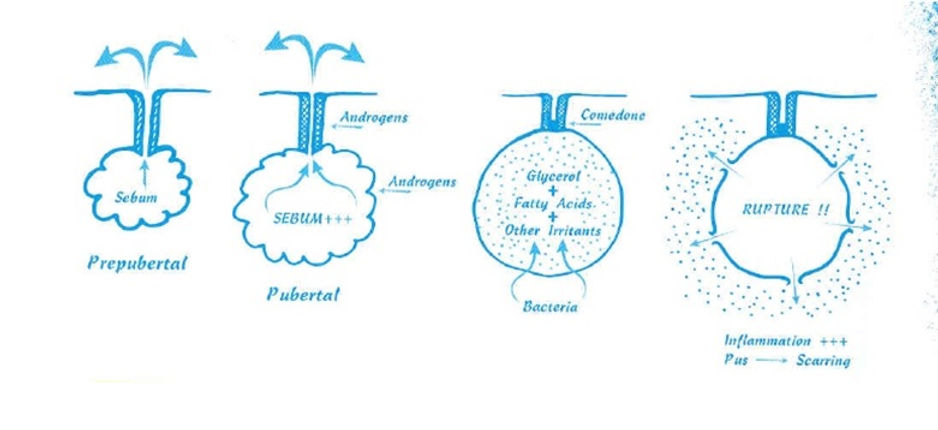
It is a skin disease in which sebum secretion is increased and pores are closed with dead skin cells, so that sebum cannot be discharged, resulting inthe formation of comedones and an inflammatory reaction occurs due to acne bacteria.
Acne is the most common skin disease that occurs frequently in adolescents as well as adult men and women in their 20s to 40s.
Acne usually occurs on the face and can also occur in areas with developed sebaceous glands such as the neck, back and chest.
4 Types of Acne
1. Comedones : Early Non-Inflammatory Acne
2. Papule : Mild to Moderate Inflammatory Acne
3. Pustule : Moderate to Severe Inflammatory Acne
4. Nodule : Severe Papulonodular Inflammatory Acne

1. Comedones : Early Non-Inflammatory Acne
When an excess of male hormone (androgene) irritates the skin, a lot of fat is secreted from the sebaceous glands next to the hair follicle.
In addition, as the hair follicle wall regenerates faster, a lot of keratin breaks out.
In this state, a hard mass is formed in the hair follicle as keratin and fat are mixed.
It is still not inflamed, but it appears as acne on the face.
#Closed Comedones or Whitehead
White particles of about 1 to 2 mm are formed just under the surface of the skin in a dodling manner.
A condition in which the pores are clogged and the sebum hardens and begins to protrude out of the surface
#Open Comedones or Blackhead
When some of the whitehead's contents come out of the skin through the pores, it comes into contact with air and the tip turns black.

2. Papule : Mild to Moderate Inflammatory Acne
When a germ that feeds on fat in the comedones of early acne is infected, it becomes inflammatory acne.
When the comedones becomes inflamed, the comedones bursts and the contents rise to the surface of the skin, and the inflammation begins to worsen.

3. Pustule : Moderate to Severe Inflammatory Acne
It is a small, round shape similar in size to a Papule, but contains a pus inside.
This is the result of an inflammatory reaction caused by chemical stimulation by components such as free fatty acids in sebum.

4. Nodule : Severe Papulonodular Inflammatory Acne
Clumped skin (nodules) is the most severe form of acne, which is large in size, inflamed, and contains a large amount of pus.
The contents inside the comedones escape and induce an immune response to the surrounding skin tissue, thereby forming pus.

Principles of Acne Treatment
1. Skin Cleansing
It makes skin clear and clean by removing dead skin cells that block pores from clogging with mild cleaning ingredients.
2. Control Excess Sebum
It suppresses the production of excess sebum, a major cause of acne.
3. Antibacterial Effect
The antibacterial agent actively improves and prevents skin problems by playing a continuous and broad antibacterial role against various kinds of bacteria and fungi that are harmful to the skin.
4. Skin Soothing
It relieves red marks and traces caused by inflammation and promotes skin regeneration.
Causes of Acne
Increased sebum secretion by androgen stimulation
Dyskeratosis in the hair follicle
Proliferation of acne bacteria (P. acnes)
Inflammatory reaction

